Shock treatment, or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), is not a new way of treating depression. ECT treatments have become pretty commonplace in some areas.
An ECT treatment is not the same as simply shocking someone when they display signs of depression. Rather, this form of therapy is reserved for treatment-resistant depression.
Keep reading to find out more about this method and how it is incorporated in the programs at Emerald Isle Health & Recovery!
Free Mental Health Assessment
What is depression?
Table of Contents
Depression is a serious mental illness characterized by persistent low mood and diminished interest or pleasure in daily activities. It affects an estimated 15 million American adults, more than 6 million of whom have had at least one major depressive episode.
An estimated 2-3% of children and adolescents experience at least one major depressive episode before age 18, and approximately half of them will have another episode during adulthood.
Even though it is commonly diagnosed in adults, the condition among children and adolescents is on the rise. The World Health Organization estimates that the lifetime prevalence of this illness (if not treated) is about 13%, with rates varying from 4% in Japan to 18% in France.
The Definition of Clinical Depression
This is not the same as being unhappy or in a bad mood, according to the American Psychiatric Association (APA). For example, you may feel sad for an hour or so when something terrible happens—your mood may lift, and you may be happy again.
You may also feel anxious or stressed for a certain period of time—but then that feeling goes away. The truth is that this is one of the most severe mental health conditions.
Severe depression is distinguished from normal sadness or anxiety by its intensity and persistence over time. Anyone experiencing the symptoms should seek support and engage in mental health care immediately.
What are some of the symptoms of depression?
Many people think of depression as being one of the “invisible” psychiatric disorders. The truth is that the more severe symptoms of waning mental health are actually fairly easy to spot once you have an awareness of what they are.
- Loss of Hope – This is one of the more common symptoms for persons to experience. If you notice in yourself or a loved one a pattern of thoughts or expressing feelings of being helpless, being wracked by guilt, or just generally feeling unable to cope with life and a lack of enthusiasm, it might be time to get screened.
- Fatigue, Insomnia, and General Physical Pain – This illness sn’t just in your head, it actually manifests physical symptoms. These can be debilitating at times. If you notice a persistent pattern of feeling fatigued and tired, or even excessive body pains when you’ve not actually exerted your body physically to warrant it, this may be an indicator. Chronic insomnia can also be a strong sign.
- Changes in Weight and Appetite – Barring any external life changes that can act as an explanation, if there is a sudden drastic change in either weight and/or appetite (this can be an increase OR a decrease), it may suggest mental health struggles.
- Behavioral Changes – Persons suffering from serious mental illness oftentimes experience changes in behavior so drastic that it can be perceived as an actual change in personality. In men, this may manifest as a drastic increase in irritability. These changes can also look like isolation or even becoming more sullen and aggressive.
What other psychiatric disorders include depression as a co-occurring condition?
Depression in and of itself can actually be a condition experienced as a result of other mental health conditions. For example, anxiety and depressive disorders are usually co-occurring with neurodivergent persons (persons diagnosed with ADHD and/or Autism).
This is because neurodivergent persons usually struggle to integrate neatly and easily into the world and so, develop generalized anxieties and depressive tendencies. However, conditions like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and borderline personality disorder, to name a few, can also be responsible for the presence of a depressive condition.
What sort of treatments exist for depression?
There are many different treatments available to treat major depression, but the most effective treatment option is often a combination of several different techniques to achieve the greatest effect. It’s not uncommon for other treatments to be used alongside the main treatment methodology.
The Efficacy of Medication for Depressive Symptoms
Antidepressant medications remain one of the most effective treatments available, and they can be used alone or in conjunction with other treatments. They are designed to correct the chemical imbalances in the brain that cause major depression, and numerous studies have proven their effectiveness.
However, antidepressants can have side effects and should not be used as a first-line treatment, especially since they take time to work. Antidepressants should be used in conjunction with other practices, such as CBT or interpersonal therapy (IPT), which focuses on interpersonal relationships and communication patterns.
What is treatment-resistant depression?
Treatment-resistant depression refers to cases where individuals who have tried at least two different treatments for major depression are still experiencing symptoms. This can be frustrating for both the person suffering and their loved ones, but it is important to remember that this is not a hopeless situation.
It takes time, effort, and patience, but there are other therapies that have been proven to work as effective treatments to overcome this hurdle.
Let’s talk about Electroconvulsive Therapy
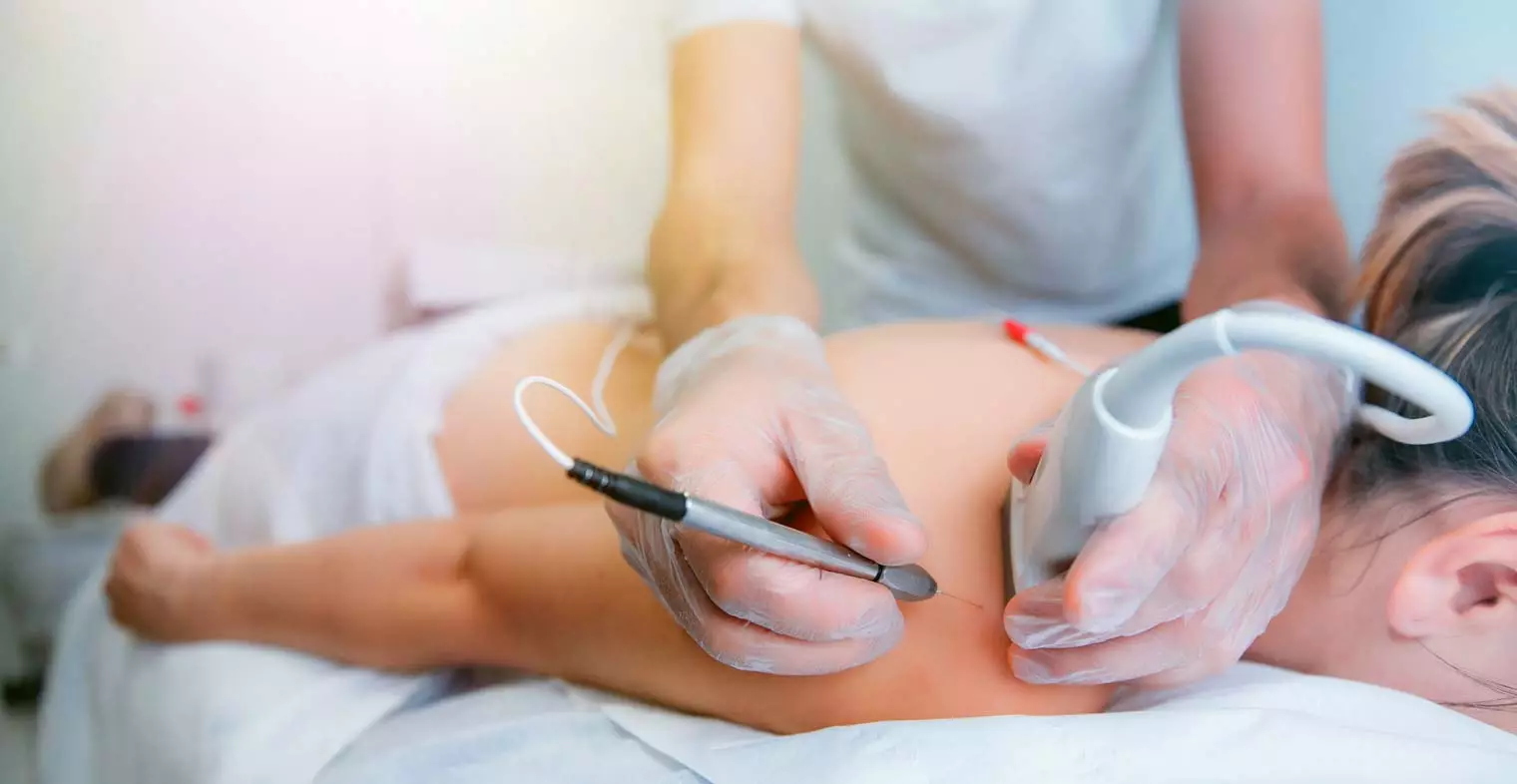
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical procedure used for severe depression that is not responding to any other treatment. Ect treatments have been around since the early 1940s and have since become an alternative to treat depression. T
he idea was that electrical stimulation would cause brain stimulation which leads to activity and would pull a person out of their depression. One of the accepted side effects that were known since its early use was slight memory loss.
24 Hour Mental Health Hotline
How Does ECT Therapy Work?
While the precise mechanism of action is unknown, it is widely believed that using electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) causes small seizures in the brain through transcranial magnetic stimulation. Patients are awake during both the process of putting them under general anesthesia during their ECT treatment, but they experience no pain or discomfort other than some muscle stiffness.
Prior to administering electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), patients are given a series of medications orally or through an IV that puts them into a controlled state of seizure akin to that of persons who have seizure disorders. The patient’s heart rate slows down and blood pressure drops in order to keep them safe while they’re unconscious. Electrodes are then affixed to the patient’s head, and electrical pulses are passed through them in order to induce a seizure.
During this time, many patients typically feel a tingling sensation throughout their bodies. Once the seizure has ended, the patient wakes up almost immediately with no side effects except for muscle stiffness—the seizure itself lasts just a few seconds!
The Clinical Evidence for Shock Therapies
There is a wealth of extensive research that has found that ECT works quite effectively for the relief of major depression. Clinical evidence indicates that in patients with uncomplicated but severe depressive disorder, ECT can produce a not insubstantial improvement. It is also used for other severe mental illnesses, such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. ECT isn’t some fly-by-night unendorsed method either. Electroconvulsive therapy has been officially recognized as a valid treatment for treating severe mental illnesses by the American Psychiatric Association, with countless cases showing substantial improvement in conditions.
Although electroconvulsive therapy is an effective option for many individuals with serious illnesses, it should be noted that it is not a cure. Many persons treated with ECT need to continue with some type of maintenance treatment. This typically means psychotherapy and/or medication or, in some circumstances, ongoing treatment by ECT, sometimes for a few months at a time before treatment ends.
The Pros and Cons of ECT
All treatment plans (including ECT) have their own risks and benefits. Treatment by ECT is no different. To discuss this, we need to examine exactly what ECT work is doing to the brain. Keep in mind that this is actual electrical stimulation being applied to the brain when ECT is used. This brain stimulation is the key to why the ECT method works.
With full transparency, ECT has been associated with short-term memory loss. Some people can have trouble remembering events that occurred in the days, weeks, or months prior to undergoing ECT treatment. For the vast majority of cases, the memory problems improve within a couple of months. Very rarely have persons expressed permanent gaps in memory or memory loss after ECT.
Does ECT require General Anesthesia?
ECT requires, as with most other surgeries, the employment of general anesthesia is used for The most common side effects of ECT on the day of the procedure itself have been said to include nausea, headache, fatigue, confusion, and slight memory loss, which may last as little as a few minutes to a few hours.
For some patients, the risks of ECT may be less than those of ongoing treatment with medications. ECT can work more effectively and more quickly than medications. It can be especially useful if a patient is suicidal or even has not been responding to other forms of care.
ECT isn’t typically used as a first resort for many cases. However, using ECT becomes more important if there is little response to other therapies.
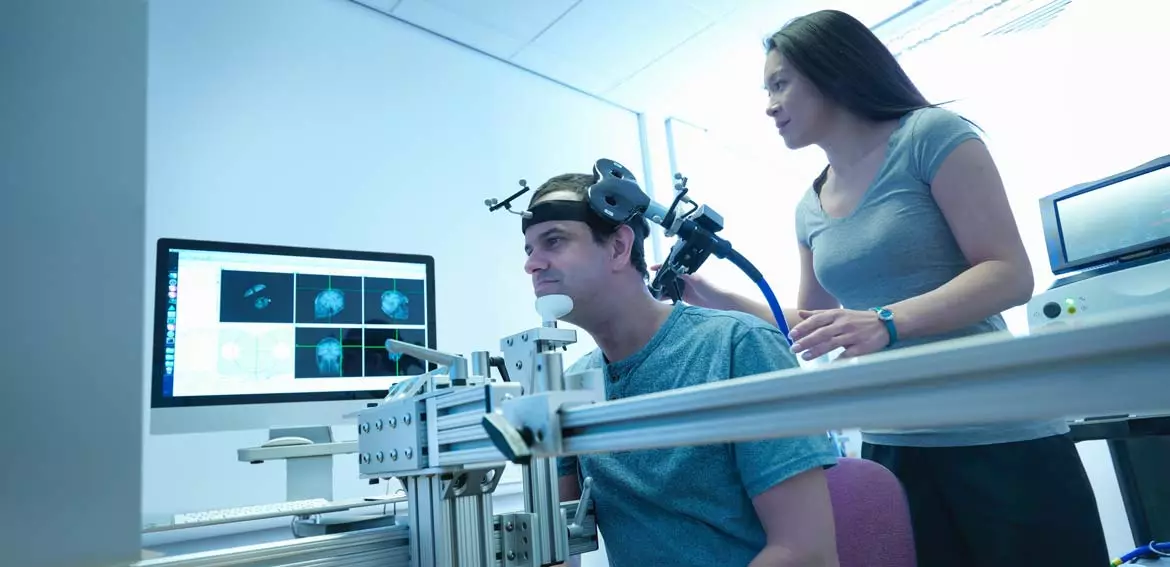
TMS as a method of treating severe depression
ECT is not the only alternative therapy option that is available for persons who aren’t responding adequately to traditional methods.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS), for instance, can be used in cases with a low response to other forms of care. This method involves quickly alternating magnetic fields which result in stimulation of targeted and specific areas of the patient’s brain.
Unlike ECT, this is a noninvasive process that the patient remains conscious for and does not induce any form of seizure. The side effects of this treatment are mild and can include muscle twitches, pain at the point of stimulation, and headaches. Usually, this treatment is experienced up to five times a week for as long as a six-week cycle.
Immediate Placement for Mental Health Treatment
Other alternative therapies for depression
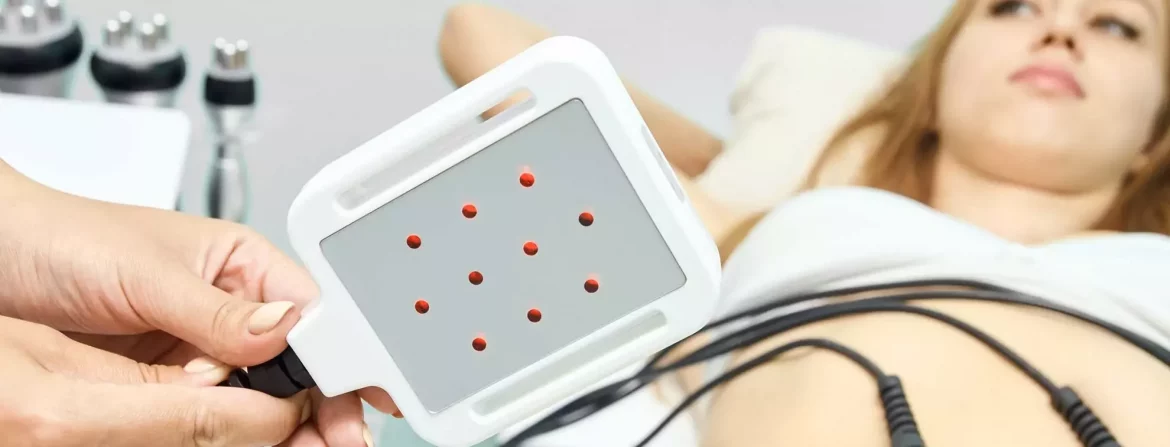
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) is yet another option that is also used to treat depression not responding to traditional methods. This practice involves the implantation of an electrical pulse generator under the skin in the patient’s chest. This uses electricity to occasionally stimulate the vagus nerve in the neck.
As with any therapeutic method, all clients must make the decisions that they are comfortable with. It should be noted that the major governing health bodies have not found any links between ECT and other alternative therapies and lasting damage.
Find Freedom from Treatment Resistant Mental Disorders at Emerald Isle
At Emerald Isle Health and Recovery, we explore all forms of effective and evidence-based forms of treatment to promote outstanding results for our clients.
If you are curious about ECT, or any of the other methods of treatment we practice in providing a top choice for holistic treatment, reach out now to discuss how we can help with our Admissions team. Your health and happiness could be a simple phone call away!